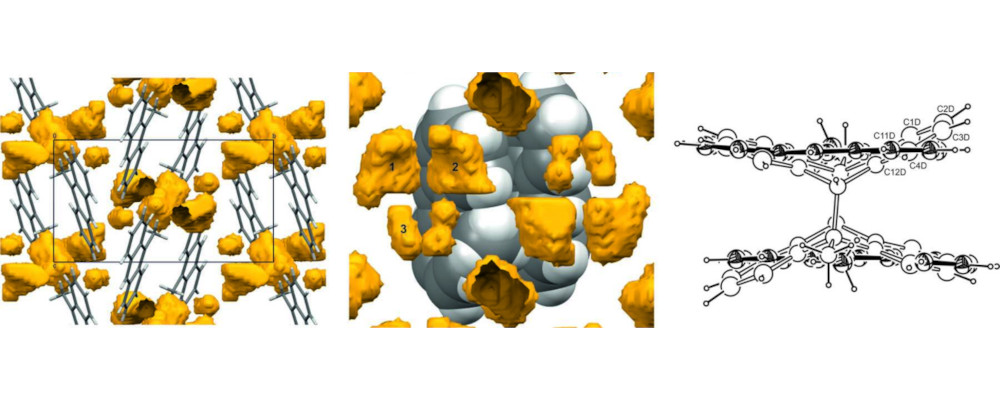
The influence of pressure on the course of [4+4] photodimerization in crystals of 9-methylanthracene is presented. The studies were performed at 0.1 and 0.4 GPa. As a result of the reaction at high pressure, crystals of the pure product were obtained, which allowed for monitoring of the reaction until its completion. The initial increase in the unit-cell volume caused by the reaction under ambient conditions was reduced at high pressure due to the decrease in the void volume. Despite the smaller size of the void volume at high pressure, dimer molecules formed during the reaction changed the orientation of the monomer molecules in the crystal structure. The size of the voids above the terminal rings of the monomers correlates with the position of the terminal rings in the dimer. The reaction rate increased at high pressure, indicating that the decrease in the distance between adjacent monomers caused by pressure dominates over the decrease in the void volume. This distance is statistically constant as the reaction progresses, contrary to the reaction at ambient pressure.
The role of free space in photochemical reactions in crystals at high pressure – the case of 9-methylanthracene